VoiceXML |
| VoiceXML is a markup language derived from XML for writing
telephone-based speech applications.
Just as a web browser renders HTML documents visually, a VoiceXML interpreter renders VoiceXML documents audibly. You can think of VoiceXML interpreter as a telephone-based voice browser. |
|||||||
| VoiceXML’s main goal is to bring the full power of web development and content delivery to voice response applications, and to free the authors of such applications from low-level programming and resource management. It enables integration of voice services with data services using the familiar client-server paradigm. | |||||||
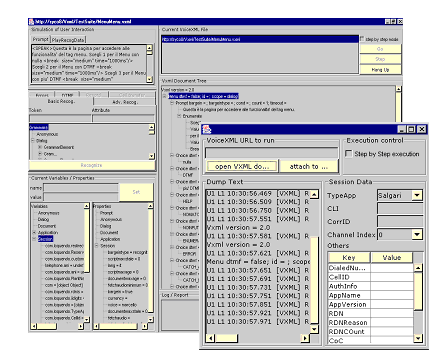
| The VoiceXML architecture contains two Java based elements:
a VoiceXML interpreter and a VoiceXML page debugger.
? VoiceXML interpreter parses VoiceXML documents and coordinates all telephone elements in order to produce voice interactions. ? VoiceXML page debugger is a GUI application - either applet based or
standalone – that connects itself to an existing interpreter session
or emulates a new session. Once connected it can show interpreter results
and meta-results in order to let developers debug their pages. |
 |
||||||
| In order to support a telephone interface, the VoiceXML interpreter runs within an execution environment that includes a telephony component, a text-to-speech (TTS) speech-synthesis component and an automatic-speech-recognition (ASR) component. | |||||||
| The VoiceXML interpreter transparently interacts with these
infrastructure components as needed. For example, text strings in output elements are rendered using TTS, telephone connection issues (picking up the incoming call, detecting a hang-up, transferring a call) are handled by the telephony component, listening to spoken input from the user and identifying its meaning is handled by the ASR component. |
|||||||
Please refer to webmaster@syco.it
for any problem regarding this page.
This page last updated on Nov 10, 2002.
Copyright © 1990-2000 SYCO S.a.s.